In what environment is the furnace used?
Furnaces may be an unfamiliar concept to many people, but this is a device used in many fields, especially in laboratories. So what exactly is a furnace, and why is it important? In this article, EMIN will share the necessary information for you to better understand this type of device, from structure, classification to practical applications in research and analysis work.
Contents
Furnaces are used in laboratories
Laboratory furnaces are specialized for generating high temperatures, often widely used in laboratories and research activities. This device is designed to heat materials and test samples effectively, meeting a variety of uses. With a sturdy structure and a heat-resistant steel outer shell, the furnace ensures fast heating speed and high durability during use.

The oven's control panel system is scientifically arranged, with an integrated electronic clock that clearly displays parameters such as actual temperature and set temperature. This helps users easily monitor and control the entire firing process accurately and conveniently.
One of the outstanding advantages of experimental furnaces is the ability to flexibly adjust factors such as temperature, firing time, and firing environment. This makes the device suitable for many different requirements in research and experiments. Oven capacities are also very diverse, from 3 liters to 30 liters, providing many choices to meet the specific needs of each laboratory.
Common types of experimental furnaces
Sort by style
- Tube furnace: Designed with a tubular furnace, this type of furnace is suitable for heating materials at high temperatures in a controlled atmospheric environment. Outstanding advantages are the ability to maintain uniform temperature and ease of handling the test sample.
- Rectangular furnace: This type of furnace has a design similar to a small cabinet with a door opening in the front, making it easy for users to put specimens inside. This is also a popular furnace line in many laboratories.
Classified by temperature range
- Maximum furnace 850°C: Operates in the temperature range from 300°C to 850°C, suitable for applications requiring medium heat levels.
- Maximum furnace 1110°C: Capable of heating from 300°C to 1000°C, meeting more diverse needs in research and experiments.
- Maximum furnace 1450°C: With a temperature range from 500°C to 1400°C, this type of furnace is used in experiments that require higher temperatures.
- Maximum 1600°C furnace: A furnace capable of operating from 500°C to 1600°C, meeting the needs of extremely high temperature firing, often used in specialized research.
Classify furnaces according to function
- Basic furnace:
This is a simply designed furnace line, with 1 to 4 temperature ranges, operating between 500°C and 1200°C. Thanks to its compact design and ease of use, the basic furnace is well suited for basic sample processing applications or laboratory ash content determination.
- High temperature furnace:
This type of oven has a modern design, supports many temperature ranges and has the ability to remember operating programs. With a maximum temperature ranging from 1300°C to 1800°C, high-temperature furnaces are often used in in-depth research, especially experiments related to materials and testing their durability under cold conditions. high temperature conditions.
- Chamber furnace:
Designed with a large heating chamber and integrated specialized air supply/exhaust system, the chamber furnace is suitable for industries that require large heat processing. This is the ideal choice when large quantities of material need to be processed or uniform high temperatures are required in the firing chamber.
- Furnace with integrated sample analysis scale:
This type of furnace is equipped with an analytical balance, helping users directly measure the mass of ash sample or the amount of volatile matter after the calcination process. This is a useful solution for experiments that require high accuracy in determining sample mass.
How to use laboratory furnaces effectively and safely
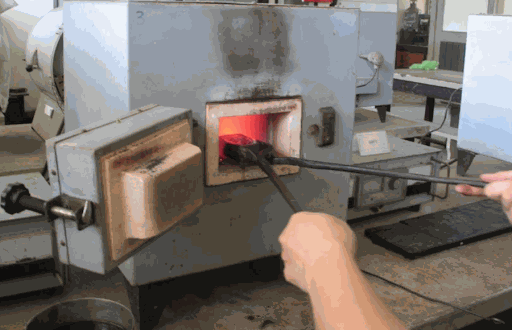
Inspect the furnace before use
Before starting, thoroughly inspect the furnace to ensure safety and efficiency. Make sure the power source is stable, the wires are not damaged, and the heating chamber is clean, with no residual material from previous use. Thermocouples and temperature control systems should be tested to ensure proper operation.
Choose the appropriate heating mode
Furnaces are often equipped with many modes to suit different requirements. Choose the correct heating mode for the temperature, time, and environment required for the material or specific experiment to achieve optimal results.
Arrange the calcined sample properly
The way the sample is arranged inside the heating chamber greatly affects the heat transfer efficiency and temperature uniformity. Samples should not be placed too tightly or too sparsely, and should be kept at a reasonable distance so that the heat spreads evenly. Place the sample in the center of the furnace and use a heat-resistant tray for easy handling after heating. The sample in the firing device should not exceed ½ of the device's volume to ensure effectiveness.
Heat up and cool down slowly
To avoid thermal shock causing material damage or danger to the user, program the heating and cooling process gradually, appropriate to the nature of the test sample.
Use protective gear when working
During the process of using the furnace, especially when taking samples, it is necessary to fully equip protective equipment such as heat-resistant gloves, goggles, and masks. This helps minimize the risk of burns or other unwanted risks.
Clean the furnace after use
After completing the process, let the oven cool completely and unplug the power source before cleaning. Regular cleaning ensures efficient oven operation and prolongs the life of the appliance.
Conclude:
With the information shared by EMIN, we hope you have a clear understanding of the structure, classification and instructions for using kilns safely and effectively. Helps you maximize the performance of the equipment, while ensuring user safety and maintaining long-term durability of the furnace.
