Sugar meter
Comparing Types of Sweetness Meters: Choosing the Right One for Your Needs
Have you figured out which sweetness meter best suits your work? From traditional mechanical refractometers to modern digital sugar meters, each type has its own advantages when it comes to measuring sugar concentration accurately. Discover their differences, pros and cons, and practical applications in this detailed comparison — and don’t miss out on the most essential tool for quality control.
What is a Sweetness Meter?
A sweetness meter is a measuring device used to determine the sugar content (Brix) in liquids. Depending on the industry, it plays a crucial role in quality control — whether it’s measuring sweetness in milk, juices, or conducting tests in healthcare. For example, a fruit juice manufacturer uses a sweetness meter to adjust formulas and ensure both taste consistency and safety for consumers.

Detailed Comparison of Sweetness Meter Types
Handheld Refractometer (Mechanical Sweetness Meter)

The refractometer offers moderate accuracy, largely depending on the user’s technique. Compact and highly portable, it’s ideal for field measurements. Affordable and easy to maintain, it suits individuals or small-scale operations.
Features:
Uses the principle of light refraction to determine Brix level.
Compact and durable, does not require electricity.
Advantages:
No batteries needed; works in any environment.
Ideal for farmers or quick in-store checks.
Low cost and easy to use.
Disadvantages:
Accuracy depends on manual handling and visual reading.
Errors may occur when samples contain impurities or dark colors.
Reference product: Kruss HR92 Handheld Refractometer (58–92%Brix,1%)
Digital Sugar Meter
Digital meters offer high accuracy and stable performance. These devices are user-friendly, with modern designs. Prices range from mid to high, depending on features. They require power supply and regular maintenance to ensure long-term reliability.
Features:
Fast, automatic measurements via electronic sensors.
Digital display for clear readings; some models offer memory storage.
Advantages:
Quick and precise results across multiple samples.
Can operate under various environmental conditions.
Premium models offer data export and PC connectivity.
Disadvantages:
Higher cost compared to mechanical models.
Requires batteries or power source; sensors need periodic maintenance.
Reference product: ATAGO PR-101α Sweetness Meter (0.0 … 45.0% Brix)
Medical Glucose Meters (Glucometer, CGM)

Medical-grade meters provide very high accuracy and are designed for specific health monitoring purposes. They are portable and ideal for personal health checks. Cost ranges from moderate to high, especially with continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices. They require regular replacement of test strips or consumables.
Features:
Mainly used for blood glucose monitoring in diabetic patients.
Advanced types (CGMs) offer continuous tracking and alerts.
Advantages:
Versatile, fast, and convenient for patients.
Some models sync with health apps for better monitoring.
Disadvantages:
High initial cost, especially for continuous monitoring devices.
Ongoing expenses for test strips and sensor replacements.
Reference product: HANNA HI 96803 Sweetness Meter (Glucose; 0 to 85%)HANNA HI 96803 Sweetness Meter (Glucose; 0 to 85%)
Refer to more Hanna, Atago, Kruss sweetness meters in Category: EMIN Sweetness Meter
Overall comparison of flow meters
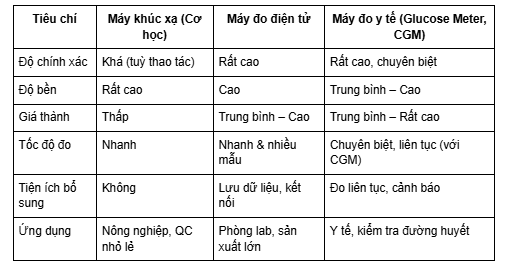
Key Considerations When Choosing a Sweetness Meter
Nature of work: Do you need quick field testing or large-scale lab analysis?
Required accuracy: For industrial production, prioritize digital devices.
Budget: For small shops, a refractometer may suffice. For businesses, a digital meter is a long-term investment.
Warranty and origin: Choose reputable brands with clear support policies.
Expandability: Modern digital meters often feature data connectivity, optimizing quality control processes.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
